Branded Apps
What Is a Native App? (A Beginner’s Guide + Examples)
A native app is an app that can be downloaded to your mobile device, offering several advantages over web apps
Author
Mighty Team
Last Updated
December 22, 2025

With over 60% of all web traffic coming from mobile, 3.5 million apps in the Google Play Store, and 1.6 million in the App Store, native apps are exploding in popularity.
In this article, we’ll explain what a native app is, how it’s different from a web app or hybrid app, and show you some examples of native mobile apps.
What is a native app?
A native app is any app that can be downloaded and live on your device; it functions as a stand-alone program and often accesses different features of your device to work. Even if products or programs can be accessed online as web apps (e.g. a social media platform), native apps aren’t just copies of the website. They have to be independently developed.
For example, when you log on to Facebook on a web browser on your laptop, you’re using different software than when you access Facebook’s native app on your phone–even though they look and feel similar.
Native applications can be made for any device; for example, your PC laptop probably has apps like photo editing or music players that work whether you’re connected to the internet or not. But usually, when we think of native apps, we’re talking about native mobile apps.
What is a web app?
A web app is a software application that is accessed through a web browser, dynamically building the content you see. When you access a site like Facebook, MSNBC, or YouTube, you don’t see the same thing as any other person. The site is built for each user.
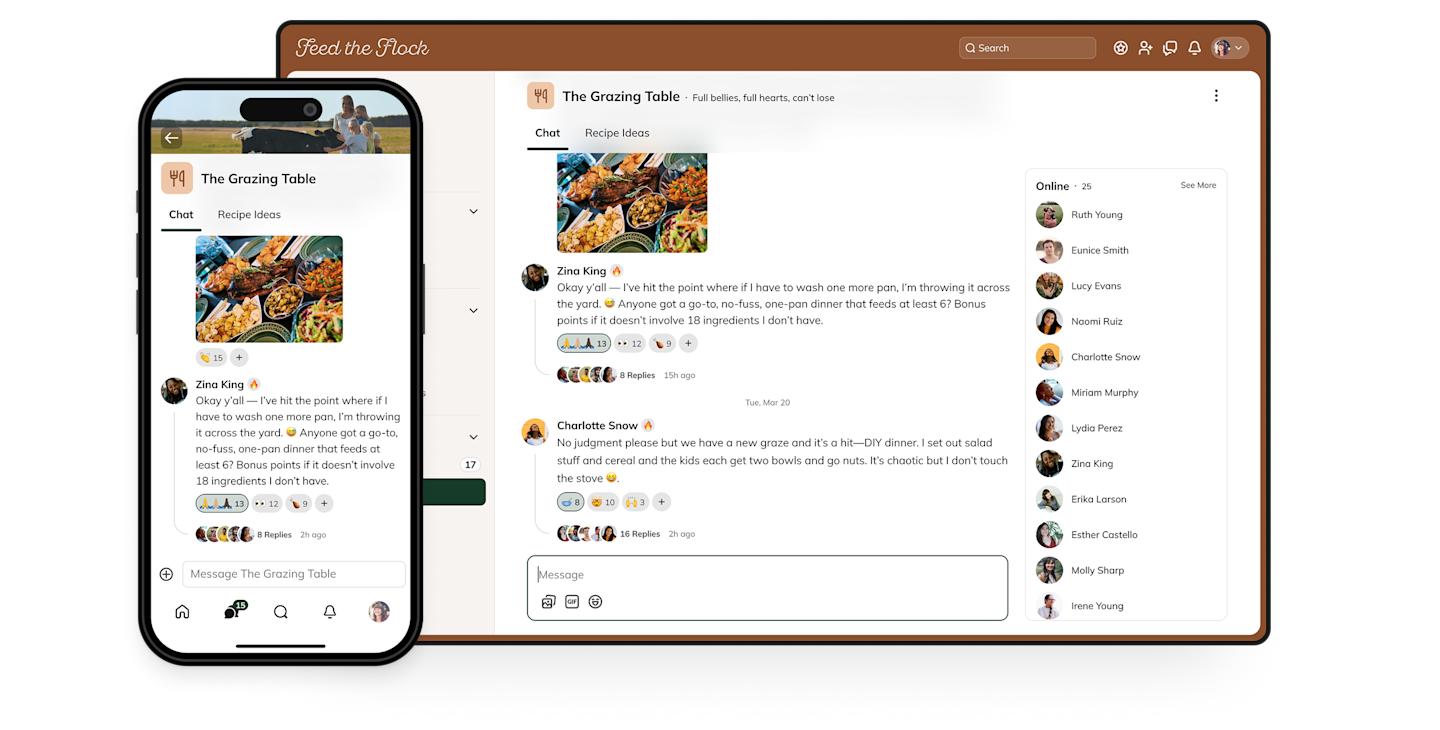
What is a native mobile app?
A native mobile app is software that’s developed specifically for the operating system (OS) of your phone–and 98.7% of phones run on either Android or iOS. It will live on your device, storing the data it needs to operate and integrating with the native features of your phone (e.g. camera, GPS, or microphone).
You need a unique native mobile app for each operating system your users have: most companies develop both Android and iOS apps.
Looking for your own native app built around community?
Advantages of a native mobile app
Uses less (or no) bandwidth
Can often be accessed offline
Works faster with better UX
Can use device tools (e.g. camera)
Better security
Higher engagement (because of ease of access & notifications)
Searchable in the Google Play and/or App Stores.
Disadvantages of a native mobile app
More expensive
Must be built for each OS
Takes up space on your device
Requires upgrades and maintenance
Differences between a native app vs web app
A native app is developed for your mobile device, while a web app usually exists in code and is accessed via a web browser. While your social media site might look sort of the same whether you access it on your computer or through an app on your device, you are functionally accessing two different things. That’s why they often have different features; for example, many social media platforms have live streaming in their apps but not on their website.
Native apps can often be accessed offline because they store relevant data on your phone. Web apps require the internet and they don’t store files on your computer.
A hybrid app mixes these two things on your mobile device, requiring some access to your hard drive and device features, but also using the HTML of a website to display within the app and therefore requiring internet access.
Web Apps | Native Apps | |
|---|---|---|
Lives on Your Device? | - | |
Uses browser code? | - | |
Custom-developed for each device? | - | |
How does it work? | Browser grabs data from server | App grabs data from device storage and sometimes from the server |
User experience? | Not great. It depends on the device and browser. | Customized to fit each device |
User Engagement | Lower, because it’s hard to use. | High (native notifications & features) |
Differences between mobile apps vs. web apps vs. hybrid apps
The main difference between mobile apps vs. web apps is that a mobile app lives on your device while a web app must be accessed through a browser. But there’s another category: we call them hybrid apps. A hybrid app uses a shell of a native app but then loads a website’s code within the app. There’s less development, but also less customization.
Web Apps | Hybrid | Native Apps | |
|---|---|---|---|
Lives on Your Device? | - | ||
Uses browser code? | - | ||
Custom-developed for each device? | - | ||
How does it work? | Browser grabs data from server | App grabs data from both storage and server | App grabs data from device storage and sometimes from the server |
User experience? | Not great. It depends on the device and browser. | Customized to fit each device | Customized to fit each device |
User Engagement | Lower, because it’s hard to use. | High (native notifications & features) | High (native notifications & features) |
Examples of native apps
Community apps (e.g. Mighty Networks)
Mobile banking apps (e.g. Discover)
Social media apps (e.g. Instagram)
Language learning or flashcard apps (e.g. Duolingo)
Productivity apps (e.g. Monday)
Creativity apps (e.g. Adobe Lightroom)
Personal finance Apps (e.g. Credit Karma)
Do you need a native mobile app?
You might need a native mobile app (or hybrid app) if one or more of these statements is true:
Your web app isn’t functional or optimal on a smartphone.
You want the best possible mobile user experience (e.g. log-on, browsing).
You want higher engagement with easier access and notifications.
You want to use a phone’s built-in features (e.g. GPS for a fitness app)
You want a mobile-only product.
You plan to monetize with mobile.
You’re selling a premium brand experience.
How to get a native mobile app?
If it’s time to develop your own native mobile app for your brand, you basically have three different approaches:
Hire developers or a development company to build a custom app. The advantage here is that you’ll get a completely custom mobile app. The disadvantage is that the cost is extremely high and you’ll need to find developers you can work with.
Work with a white-label development company. Some companies offer white-label apps. You get a premium app experience with a proven solution offered under your own brand, all at a lower price.
If you’re interested in building a mobile app that mixes courses, content, community, and events, come check out Mighty Pro! We’ve built branded apps for Jim Kwik, Drew Binsky, TED, and Cambridge University. We’ll build an amazing app under your brand, and you’ll work directly with our Mighty Pro Team who have scaled 7-figure creator brands and 8+-figure subscription businesses.
Ready to start building your community?
Start a free 14-day trial to explore Mighty—no credit card required.
More like this
Join Mighty Community
Learn the principles of Community Design™ (and see them in action) alongside thousands of creators and entrepreneurs. It's free to join!
Online Courses
Creating a Course
Teaching a Course
Course Platforms
Selling a Course
Communities & Memberships
Community Platforms
Managing a Community
Building a Community
Growing a Community
Monetizing a Community
Creators & Entrepreneurs
Monetization
Content Creation
Starting a Business
Website Builders
Creating & Managing a Website
Events
Event Platforms
Hosting & Marketing Events
Branded Apps
Creating a Mobile App
Coaching Apps
Community Apps
Coaching
Mastermind Groups
Starting a Coaching Business
Coaching Platforms
Filter by Category
Online Courses
Communities & Memberships
Creators & Entrepreneurs
Events
Branded Apps
Coaching
Start your free trial
14 Days. No Credit Card Required.